Network Settings
From OpenSimulator
Cypher.Black (Talk | contribs) |
m (→These ports must be open on any box running a simulator that attaches to a grid:) |
||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
==These ports must be open on any box running a simulator that attaches to a grid:== | ==These ports must be open on any box running a simulator that attaches to a grid:== | ||
| + | * TCP/8895 - Needed for region to region communications | ||
* UDP+TCP/9000 - Default First Simulator - grid, regions, and clients talk to these | * UDP+TCP/9000 - Default First Simulator - grid, regions, and clients talk to these | ||
* UDP+TCP/9001 - Default Second Simulator - grid, regions, and clients talk to these | * UDP+TCP/9001 - Default Second Simulator - grid, regions, and clients talk to these | ||
Revision as of 14:57, 2 December 2008
OpenSim/Grid can be pretty tricky when it comes to setting it up on a private network this document covers what OpenSim needs in terms of network resources.
Contents |
Ports used by OpenSim
Grid
- TCP/8000 - Reserved
- TCP/8001 - Grid Server - Regions and other grid services talk to this
- TCP/8002 - User Server and Login Services - Clients, Regions, and other grid services talk to this
- TCP/8003 - Asset Services - Regions and other grid services talk to this
- TCP/8004 - Inventory Services - Regions and other grid services talk to this
- TCP/8005 - Reserved (Dispatch Services)
- TCP/8895 - needed for region to region communications
These ports must be open on any box running a simulator that attaches to a grid:
- TCP/8895 - Needed for region to region communications
- UDP+TCP/9000 - Default First Simulator - grid, regions, and clients talk to these
- UDP+TCP/9001 - Default Second Simulator - grid, regions, and clients talk to these
- UDP+TCP/900x - Each next simulator...
StandAlone
- UDP+TCP/9000 - Everything runs on this port
Initial setup
- Check your /bin/Regions/default.xml
It shows something like this:
<Config sim_UUID="1e988108-76ec-45db-b89e-4ba98905681c" sim_name="mysimname" sim_location_x="1000" sim_location_y="1000"
internal_ip_address="192.168.2.101" internal_ip_port="9000" allow_alternate_ports="false"
external_host_name="82.73.39.77" master_avatar_uuid="00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000"
estate_covanant_uuid="00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000"
master_avatar_first="test" master_avatar_last="user" master_avatar_pass="******" />- Retrieve your external_host_name
- Get your internal_ip_address (ipconfig for windows, or ifconfig for linux)
- Make sure the settings match
If you have a router in front of your internet-modem, check out NAT and Port Forwarding. Else you're good to go.
NAT and Port Forwarding
Straightforward
If your host does not have a public IP address (eg it is hidden behind a home router) you will have issues hosting grid and region servers if you plan on connecting clients to it on both sides of the router, however this can be worked around through the use of port forwarding and ip-redirecting.
- Set internal_ip_address to your local LAN-ip(e.g. 192.168.2.1) (region xml-file)
- Set the external_host_name to your external IP-Address (Not a hostname, since DNS-resolving doesn't work properly) (region xml-file)
- Forward the appropriate ports to the OpenSim-server on both UDP and TCP (router-setup)
- Reroute traffic for Linux:
- iptables -t nat -A OUTPUT --dst $EXTERNAL_IP -p tcp --dport 9000:9010 -j DNAT --to-destination $INTERNAL_IP
- iptables -t nat -A OUTPUT --dst $EXTERNAL_IP -p udp --dport 9000:9010 -j DNAT --to-destination $INTERNAL_IP
Those iptables lines will redirect any traffic going to $EXTERNAL_IP on ports 9000 to 9010 to $INTERNAL_IP. The internal ip is the LAN-IP of your server, and External ip is your internet IP. Use the above iptables command on all internal machines except your gateway/router. This assumes your gateway/router machine does not also host your sim. This also assume you have a default ACCEPT policy on your internal machines. So to connect from within your LAN, use the above iptables commands to reroute the traffic to the server internal ip.
- Reroute traffic for Windows:
- netsh (please find out how this works!)
- note from paulieFlomar: I tried using Windows built-in tools like FireWall, netsh, and IP Security Policy. My experience with these tools was unsuccessful. I then tried to create an outgoing rule with some third-party firewall products. I tried ZoneAlarm and Sunbelt Firewall. Neither of these products would allow me to create outgoing rules. Finally, I tried creating an outgoing rule in my Linux IP Tables firewall. This worked. I created 2 rules which I placed in a firewall script, before my NAT rule. The rules were:
- netsh (please find out how this works!)
iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING --dst 68.185.20.134 -p tcp --dport 9000:9010 -j DNAT --to-destination 192.168.2.100
iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING --dst 68.185.20.134 -p udp --dport 9000:9010 -j DNAT --to-destination 192.168.2.100
These rules worked. I can now access my region from my LAN.
Optional:
- Register an external domain-name (for external connections)
- Use Bind for internal domain-name resolving
DynDNS loopback
This method was used and successfully tested using www.dyndns.com (creates a virtual domain for your pc/ip, like yourcomputer.ath.cx) as loopback for devices on a LAN with three machines (pentium 2.8ghz running windows xp - internet server , amd opteron running ubuntu 7.10 64bit - as opensim server - and MacBook with OSX 10.4.11 - as client), a modem (thomson/alcatel speedtouch 330) and a mini-switch (which brand no one ever heard of). The connection of these machines is made as following: Modem -> Win Pc -> Switch -> Mac and Ubuntu. Dyndns is used to loopback to the Win Pc, and then it forwards the request to the internal LAN opensim server, which grants everything for the client. As for the client, if he is inside the private LAN then he is now actually someone on the internet requesting for access to the opensim server. Thus, if the client is someone on the internet then he will be treated like that. Tricky ? Further details ahead:
Method:
- Set the simulator listening IP address to your dyndns domain - edit opensim/bin/Regions/default.xml; and change the external_host_name to external_host_name="yourcomputer.ath.cx". Leave internal_ip_address "0.0.0.0" and port "9000".
- Set the client (SecondLife Viewer) -loginuri to "yourcomputer.ath.cx:8002" (the port used was 8002, yours can be different if you configured it that way) - i didnt used the -loginserver flag also.
- Port Forward the above ports on the internet server (in this case, win xp). You do so by creating exceptions in Windows Firewall for the above mentioned ports, and for both connections: Internet Connection and LAN - this keeps the ports open for the web requests to travel over the private network.
- Edit "hosts" file (on windows, this is C:\Windows\System32\Drivers\etc\hosts and on Unix-type systems, this is /etc/hosts) entry on your internet server (in this case, win xp box) and add the following line: xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx yourcomputer.ath.cx. Of course, xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx is your opensim server internal LAN IP.
yourcomputer.ath.cx is now available for everyone to connect and you may login with the client!
DynDNS and the free IPCop Linux Firewall
Here an other way with the IPCop Linux Firewall, DynDNS and a OpenSimulator server
- Setup an IPCop firewall with 3 interfaces (red, green, orange) and put the OpenSimulator server on the orange interface (all OpenSimulator server's on one Linux box). Red is the internet, green is your lan.
- Setup the DynDNS service on the IPCop Firewall.
- change the external_host_name in the default.xml to the DynDNS name
- do'nt change the internal_ip_address in the default.XML, it should be 0.0.0.0
- if there, delete all loopbacks in /etc/hosts only 127.0.0.1 should be localhost
- customize the Port Forwarding on the IPCop Firewall (8002 TCP, 9000 UDP/TCP and for every additonal region 900X UDP/TCP). Port forwarding should be set to the (orange) interface adress of the OpenSimulator Box
Then it should be possible to conenct from inside the LAN (green) and it is also possible to conenct from the internet (over the red interface). (well, the inside-lan connections are also made now over the RED interface, but infact, this is in the same ISP network, it should be quit fast ;-)
- Attention : the ports on the IPCop Firewall must also be open if you connect from inside (green) to your OpenSimulator Grid !
If you are using the OS WebGui, do'nt forget to set the "SMTP AUTH" in your email server. Most of the dynamic IPs are blocked at ISP level so the new users do'nt get any confirmation email.
This was tested with the Hippo OpenSim Viewer and with the Login URL : http://DynDNSName:8002
Local connections with ZyXEL DSL modem/router and NAT/Port Forwarding
This solution works with the ZyXEL Prestige 660ME-61 DSL Router. It may work with other models made by ZyXEL.
Method:
- Connect by TELNET to your ZyXEL DSL modem. Use the same IP address that you would if you were using the web interface. For example, the default ip on most Embarq ZyXEL DSL modems is 192.168.2.1.
telnet 192.168.2.1
- Enter your password. If you do not know it, try just pressing <ENTER> or ask your ISP for the password. They may or may not give it to you.
- Select menu option "24. System Maintenance" from the menu.
Copyright (c) 1994 - 2004 ZyXEL Communications Corp.
Prestige 660ME-61 Main Menu
Getting Started Advanced Management
1. General Setup 21. Filter Set Configuration
2. WAN Backup Setup 22. SNMP Configuration
3. LAN Setup 23. System Password
4. Internet Access Setup 24. System Maintenance
25. IP Routing Policy Setup
Advanced Applications 26. Schedule Setup
11. Remote Node Setup
12. Static Routing Setup
15. NAT Setup 99. Exit
Enter Menu Selection Number:
- Select menu option "8. Command Interpreter Mode" from the menu
Menu 24 - System Maintenance
1. System Status
2. System Information and Console Port Speed
3. Log and Trace
4. Diagnostic
5. Backup Configuration
6. Restore Configuration
7. Upload Firmware
8. Command Interpreter Mode
9. Call Control
10. Time and Date Setting
11. Remote Management
Enter Menu Selection Number:
- At the prompt type "ip nat loopback on".
Copyright (c) 1994 - 2004 ZyXEL Communications Corp. Sprint > ip nat loopback on
- At the prompt type "exit".
Sprint> exit
- Select menu option "99. Exit"
- Follow all other steps for configuring and starting your server as outlined in Getting Started.
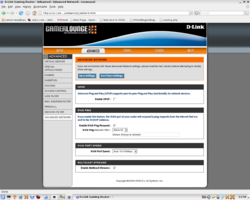
Local connections with the DLink GamerLounge Extreme N router
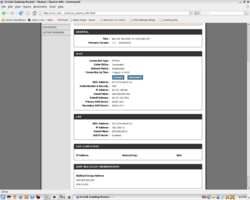
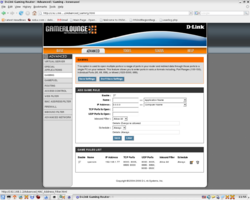
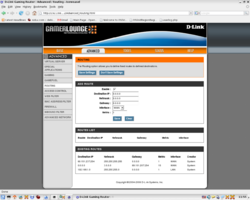
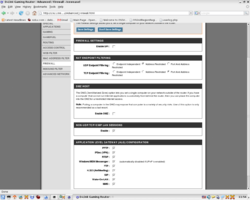
Networking and router configurations have been responsible for 98% of all trouble I have had setting up and operating OpenSimulator region server software. Insuring that you have a capable router properly configured should be the first thing on the list of configuration checkpoints for a smooth and trouble-free path to OpenSimulator software operations in GridMode.
Below is a series of screen snapshots with the key pages of my router configuration interface with proper settings displayed.
The settings below assume that you have an otherwise working connection and do not touch on such subjects as port conflicts or logging your network onto your ISP's provider network.
- provided that all information supplied in ~opensim/bin/OpenSim.ini and in your ~opensim/Regions/*.xml are properly configured, this should have you up and running.
NOTE: Contrary to what is displayed above, DHCP services are not required to operate OpenSimulator server software.