OpenSim.Region.ScriptEngine.DotNetEngine
From OpenSimulator
(→Places to extend script support) |
m (→How it works) |
||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
For example: | For example: | ||
Event for loading a script will be processed and EventManager will tell ScriptManager to load the script. | Event for loading a script will be processed and EventManager will tell ScriptManager to load the script. | ||
| − | Event such as touch_start is received in EventManager then sent to EventQueueManager that will tell SCriptManager to execute the touch_start function in the script. | + | Event such as touch_start is received in EventManager then sent to EventQueueManager that will tell SCriptManager to execute the |
| + | touch_start function in the script. | ||
Note! If event is for a particular object, EventQueueManager will queue event for all scripts inside that object.<br /> | Note! If event is for a particular object, EventQueueManager will queue event for all scripts inside that object.<br /> | ||
* If it is a script rez then OpenSim.Region.ScriptEngine.DotNetEngine.Compiler.LSL will compile the script to .Net Assembly.<br /> | * If it is a script rez then OpenSim.Region.ScriptEngine.DotNetEngine.Compiler.LSL will compile the script to .Net Assembly.<br /> | ||
* This assembly is loaded into an AppDomain created by AppDomainManager.<br /> | * This assembly is loaded into an AppDomain created by AppDomainManager.<br /> | ||
* EventQueueManager has a separate thread running to process its event queue. Events are actually functions inside the script .dll that is called "<state>_event_<event_name>" for example "default_event_touch_start". State is read from a global variable in the script .dll.<br /> | * EventQueueManager has a separate thread running to process its event queue. Events are actually functions inside the script .dll that is called "<state>_event_<event_name>" for example "default_event_touch_start". State is read from a global variable in the script .dll.<br /> | ||
| − | * Some commands | + | * Some commands require more time before returning, processing these is done in LSLLongCmdHandler.<br /> |
* Every script receives a private instance of LSL_BuiltIn_Commands. This is their only way of manipulating anything outside themselves.<br /> | * Every script receives a private instance of LSL_BuiltIn_Commands. This is their only way of manipulating anything outside themselves.<br /> | ||
---- | ---- | ||
| + | |||
===Places to extend script support=== | ===Places to extend script support=== | ||
* LSL_BuiltIn_Commands.cs | * LSL_BuiltIn_Commands.cs | ||
Revision as of 14:05, 11 February 2008
DotNetEngine
Namespace: OpenSim.Region.ScriptEngine.DotNetEngine
DotNetEngine is a ScriptEngine that executes LSL scripts contained within objects.
Core development blog: [1]
To look at the LSL command implementation status, go to LSL Status.
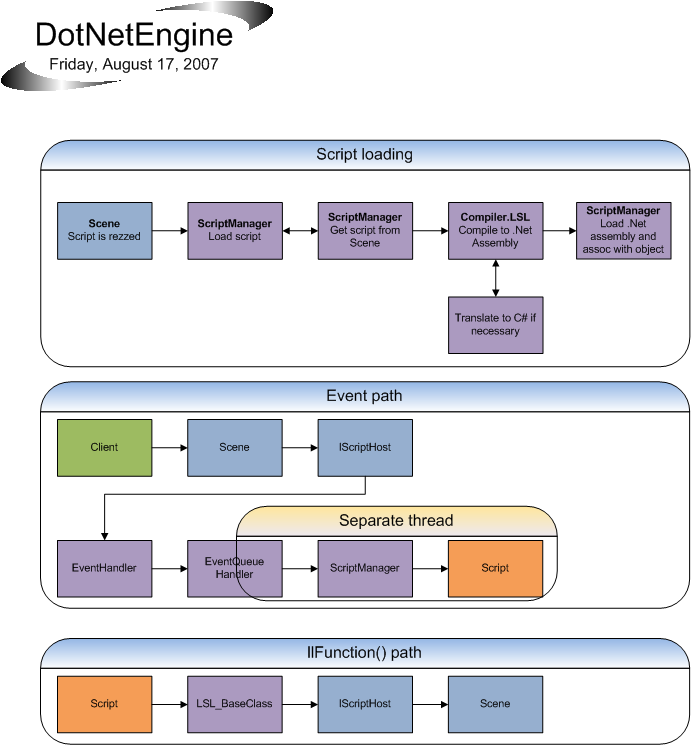
How it works
- Create instance of ScriptEngine(scene).
- ScriptEngine will create instances of:
EventManager EventQueueManager ScriptManager AppDomainManager LSLLongCmdHandler
- EventManager will hook up all necessary events. (all possible script events, script rez, script derez, etc)
- When events are received, they are processed inside EventManager.
For example: Event for loading a script will be processed and EventManager will tell ScriptManager to load the script. Event such as touch_start is received in EventManager then sent to EventQueueManager that will tell SCriptManager to execute the touch_start function in the script.
Note! If event is for a particular object, EventQueueManager will queue event for all scripts inside that object.
- If it is a script rez then OpenSim.Region.ScriptEngine.DotNetEngine.Compiler.LSL will compile the script to .Net Assembly.
- This assembly is loaded into an AppDomain created by AppDomainManager.
- EventQueueManager has a separate thread running to process its event queue. Events are actually functions inside the script .dll that is called "<state>_event_<event_name>" for example "default_event_touch_start". State is read from a global variable in the script .dll.
- Some commands require more time before returning, processing these is done in LSLLongCmdHandler.
- Every script receives a private instance of LSL_BuiltIn_Commands. This is their only way of manipulating anything outside themselves.
Places to extend script support
- LSL_BuiltIn_Commands.cs
These are the functions script can use to manipulate the scene. Commonly known as ll-functions. They are LSL functions such as llSay, llWhisper, etc. LSL Status contains up to date status on what functions have been implemented. Anyone who wants to contribute can implement a command and put a patch on the [http://www.opensimulator.org/mantis bug tracker}.
- EventManager.cs
This is where events are coming from server and being queued for scripts. All 16 or so LSL events needs to be implemented here.
This image is a bit (not much) outdated, but gives you an idea of the path script events/functions go through.